Distributed Acoustic Sensing
UDOT has one of the most robust, DOT-owned fiber optic networks in the nation. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), or “fiber sensing”, uses fiber optic cable buried in the road to monitor roadways in real time by detecting acoustic events, like crashes and avalanches, in the vicinity of the fiber. This UDOT fiber sensing project will be one of the first in the nation. It aims to provide critical safety and maintenance information more quickly than with other methods.
OVERVIEW
Distributed Acoustic Sensing is a technology that senses the tiny vibrations in buried fiber optic cable to detect events happening near the fiber. These vibrations may be caused by crashes or avalanches. Since the fiber can sense these instantly, a warning can be sent to the UDOT Traffic Operations Center immediately and operators can coordinate quick responses to these events.
BENEFITS OF THE TECHNOLOGY
Fiber Sensing allows useful information to be quickly transmitted to the UDOT Traffic Operations Center. In many instances, this information will arrive and be processed sooner than with other methods of detection. Quicker responses to the events can potentially save lives and return traffic to normal operations more efficiently. The technology also allows UDOT to keep Utah travelers informed, which increases mobility and safety.
QUICK FACTS
“UDOT’S 3,400-mile fiber optic network spans the entire state, connecting urban and rural areas and providing border-to-border coverage.”
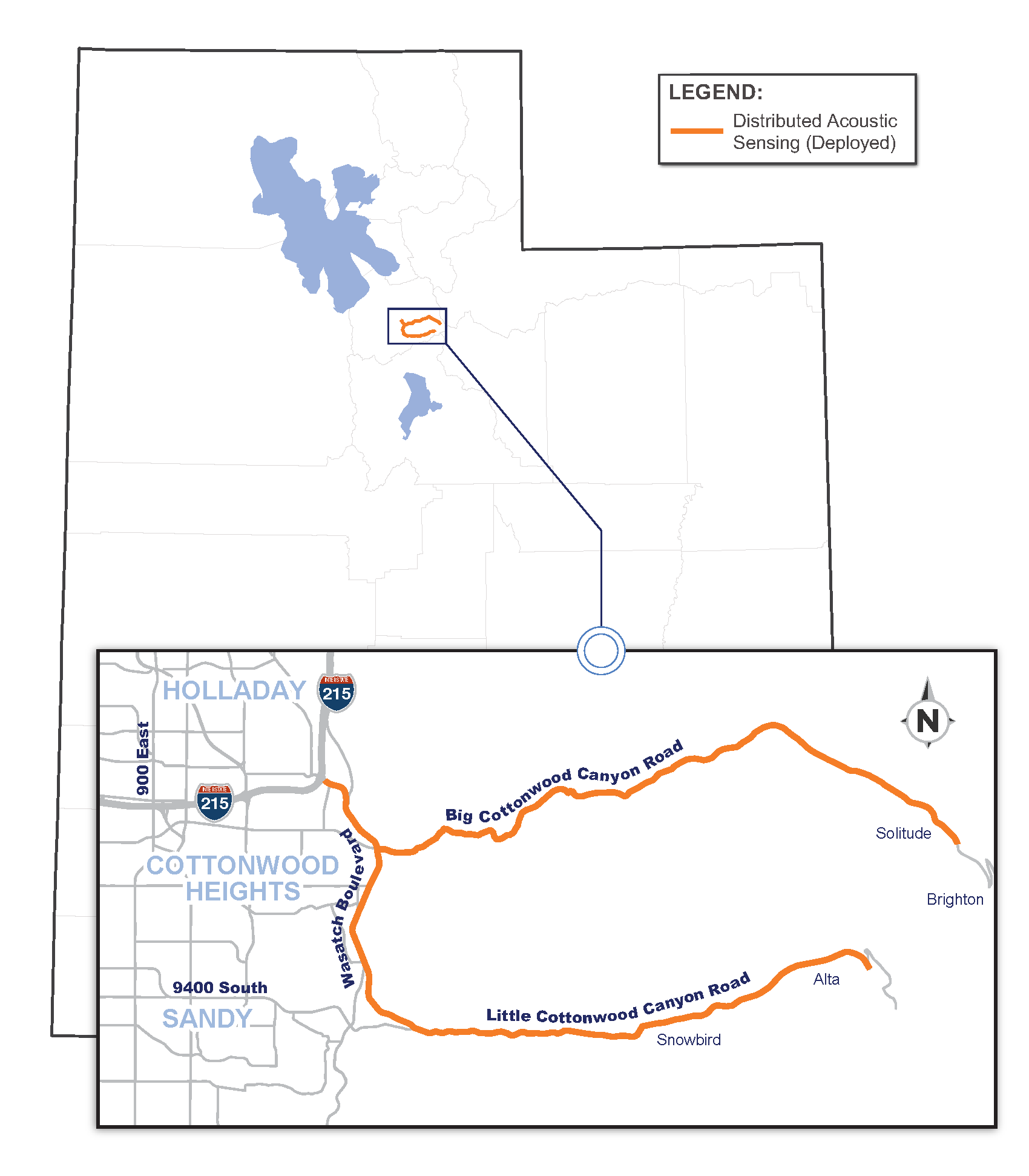
WHERE THE TECHNOLOGY IS DEPLOYED
The Fiber Sensing system is currently deployed in Big and Little Cottonwood Canyons in Salt Lake County. These canyons experience serious crashes and frequent avalanches during severe winter weather.